Palpitations
Palpitation is an awareness of the heartbeat and is very common. You may feel your heart pounding, fluttering or beating faster than normal. Although typically palpitations are felt in your chest, it is not unusual to feel them in your neck or throat. These sensations can have a variable duration and may last seconds, minutes or even hours. Even though an increased awareness of your heartbeat often does not have a serious cause, if accompanied by other symptoms, it is advisable to seek medical advice, as this may signal you have a problem with your heart.
Symptoms of Palpitations
Besides an increased awareness of your heart beating, other symptoms to be aware of when you experience this sensation in your chest include:
- Discomfort in your chest or chest pain
- Breathlessness
- Dizziness
- Feeling faint or actually blacking out
- Tiredness
- Sweating
Causes of Palpitations
Palpitation has many causes which may include:
-
Lifestyle factors such as drinking tea, coffee or other drinks that contain caffeine and consuming alcohol
-
High levels of emotional stress
-
An irregular heart beat (such as atrial fibrillation, AF).
-
Other medical conditions such as anaemia and thyroid disease.
-
Some women may also find that hormone changes during their menstrual cycle, pregnancy or around the menopause may lead to palpitations.
-
Some medications may be associated with palpitations.
Diagnosing Palpitations
If your palpitations are caused by an arrhythmia, it is important to determine the correct diagnosis so that you can be provided with the correct treatment. Failure to do so can impact significantly on your quality of life.
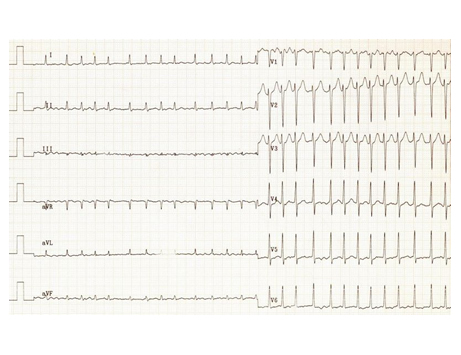
Your GP may identify abnormal heart rhythms by examining you which will then need further specialist investigation. Central to the diagnosis of any arrhythmia causing palpitations is a recording of the ECG during those symptoms.
An ECG can aid diagnosis providing that you have symptoms at the time of the recording but it may not be helpful if at that time you have none. Specialist recoding techniques, ambulatory ECG monitoring (for example 24 hour ECG recording) can be used to make the diagnosis.